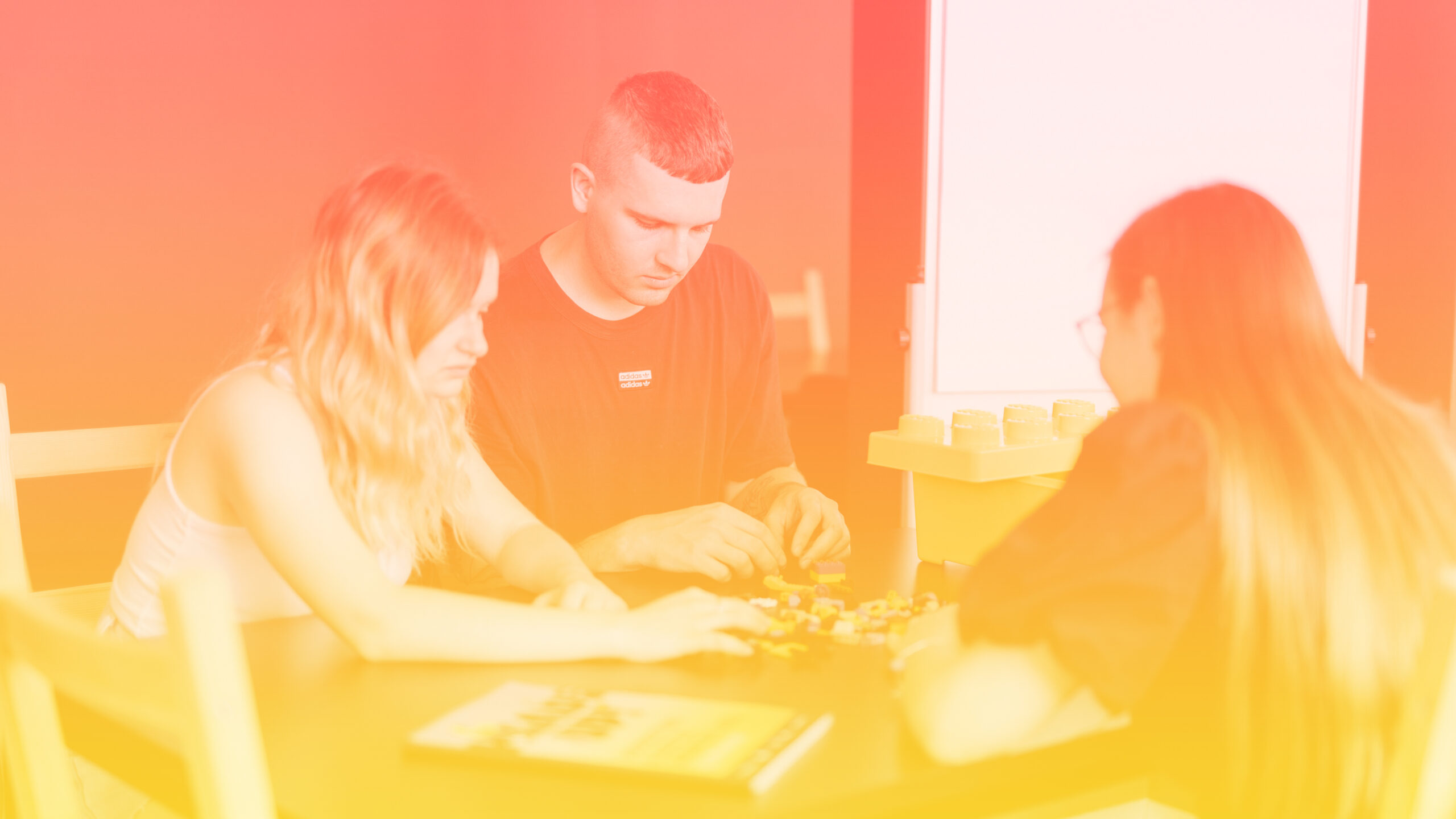
Design Thinking is an approach used for practical and creative problem-solving. Its foundations lie in methods and processes that are often utilized. This approach is applicable to a wide range of areas and is not necessarily limited to design. The first publication on Design Thinking was written by Stanford University professor John E. Arnold in 1959. Design Thinking is an approach that helps creatively solve problems with consideration for the needs of various users. This method finds application not only in management and design but also in the creation and improvement of products and services within companies. It explores user needs with empathy and seeks optimal solutions based on the insights gained. Ultimately, it contributes to the continuous improvement of the user experience with specific products and services.
The Design Thinking process itself is divided into five phases:
- Empathy Phase: This is the key element of the entire process. In this phase, it is important to focus on the needs, goals, and desires of the user to gain real information. This understanding serves as the foundation for the subsequent phases, such as problem definition and idea generation. This approach emphasizes humanity and compassion, enabling us to design solutions that are relevant and meaningful to users. Common methods used in the empathy phase include observation and empathetic interviews.
- Define Phase: In this phase, we focus on mapping what we have learned about the customer and try to find various connections obtained during the empathy phase. The goal of this phase is to clearly define the problem that needs to be addressed.
- Ideation Phase: This phase opens up space for creativity and divergent thinking, where as many ideas and solutions as possible are generated based on the previously defined problem. Various techniques such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and bodystorming are used.
- Prototype Phase: This phase is about experimenting and turning ideas into tangible products. A prototype is essentially a scaled-down version of a specific product that allows testing of functionality and effectiveness in real conditions, while also identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the prototype.
- Testing Phase: After creating prototypes, the testing phase follows, which involves verifying their functionality with users in a real environment. The goal is to determine whether the designed solutions actually solve the identified problems and provide value to the user. The results from the testing phase can then lead to adjustments or redefinition of the original problem or idea.
These defined phases form a cycle that can repeat multiple times, continually improving and adapting based on the feedback received. The infinite loop begins with understanding the user and their environment, continues with analyzing the problem and generating ideas for its solution, and then proceeds with prototyping and testing the prototypes. This allows for the adaptation and enhancement of the product.
Design Thinking offers numerous advantages. It enables the creation of solutions based on empathy and understanding of user needs. It fosters creativity and innovation in the problem-solving process. Its iterative approach allows adaptation to changing circumstances. The result is products and services that better meet user expectations and increase companies’ competitiveness. The risk of failure is reduced thanks to early-stage testing and problem-solving. Design Thinking also promotes team collaboration and synergistic performance.